Force length 1
Overview
This demo shows how to simulate steady-state length tension curves.
What this demo does
This demo runs a series of simulations in which a half-sarcomere is activated at different lengths.
Instructions
- In MATLAB, change the working directory to
<repo>/code/demos/force_length/force_length_1 - Open
force_length_1.m - Press F5 to run
Output
After the program finishes you should see a figure.
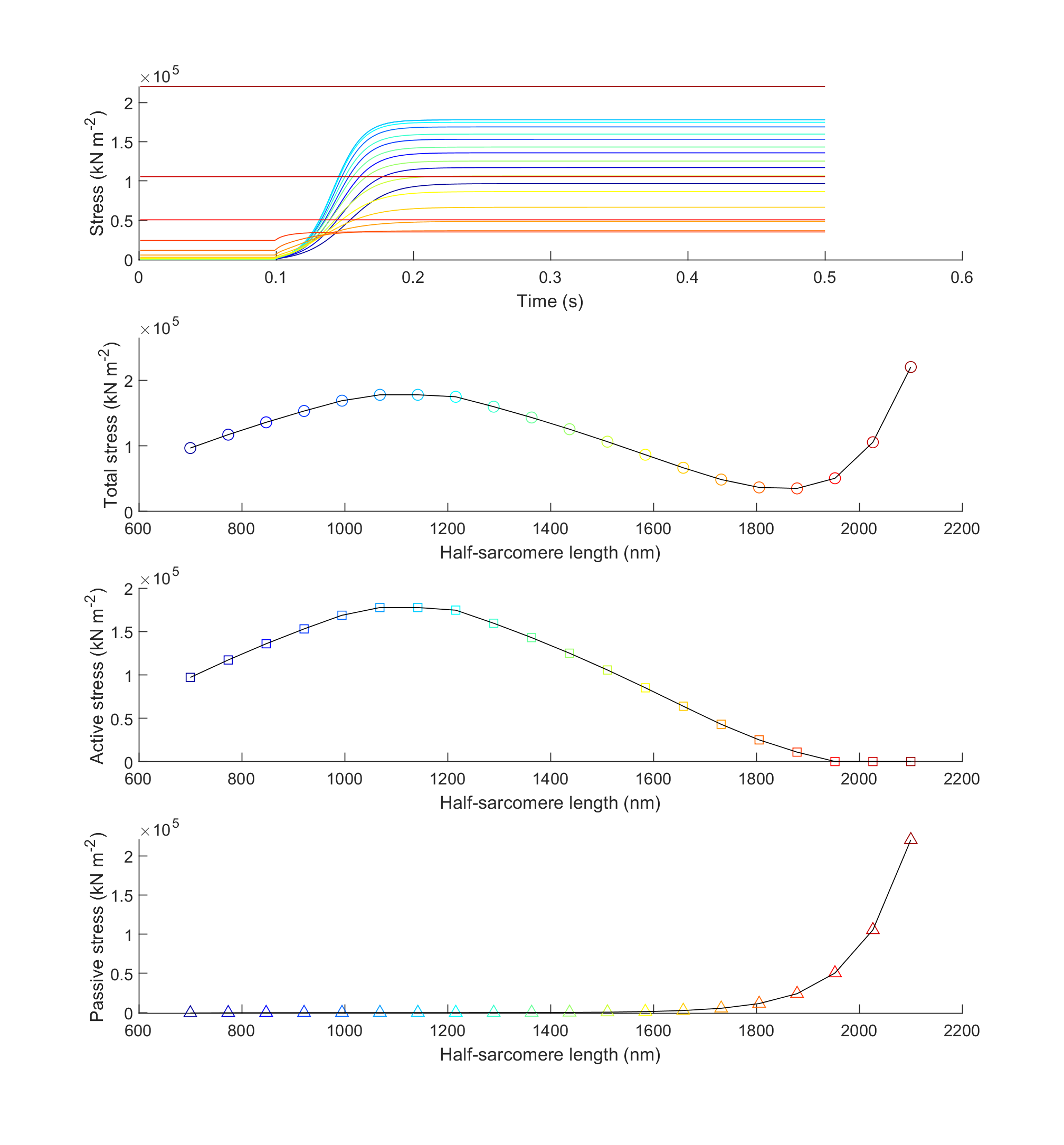
How this worked
The first section of the code sets up some variables and adds the MATMyoSim folders to the current path. Line 10 creates an array called hs_lengths that contains 20 values evenly spaced between 700 and 2000.
function demo_force_length_1
% Demo demonstrates force_length curve
% Variables
base_model_file = 'sim_input/base_model.json';
options_file = 'sim_input/options.json';
protocol_file = 'sim_input/protocol.txt';
results_base_file = 'sim_output/results';
no_of_time_points = 500;
time_step = 0.001;
hs_lengths = linspace(700, 2000, 20);
% Make sure the path allows us to find the right files
addpath(genpath('../../../../code'));
The next section generates an isometric protocol and saves it to file.
% Generate a protocol
generate_isometric_pCa_protocol( ...
'time_step', time_step, ...
'no_of_points', no_of_time_points, ...
'during_pCa', 4.5, ...
'output_file_string', protocol_file);
The next section loads the base model from file, and loops through hs_lengths, updating the base model with each new length and writing it to disk. The files for each job are stored in a batch structure.
% Load the base_model
base_model = loadjson(base_model_file);
% Create a batch structure
% Now loop through the hs_lengths
for i = 1 : numel(hs_lengths)
% Create and save a new model file for each length
model = base_model;
model.MyoSim_model.hs_props.hs_length = hs_lengths(i);
model_file = fullfile(cd, 'sim_input', 'hs_models', ...
sprintf('model_%i.json', i));
savejson('MyoSim_model', model.MyoSim_model, model_file);
% Set up the results file
results_file{i} = sprintf('%s_%i.myo',results_base_file, i);
% Add the job to the batch structure
batch_structure.job{i}.model_file_string = model_file;
batch_structure.job{i}.options_file_string = options_file;
batch_structure.job{i}.protocol_file_string = protocol_file;
batch_structure.job{i}.results_file_string = results_file{i};
end
The next section is very short and simply runs the batch jobs in parallel.
% Now that you have all the files, run the batch jobs in parallel
run_batch(batch_structure);
The final section loads the results files back into memory and plots
- force against time for each trial (top plot)
- steady-state total force against half-sarcomere length (second plot)
- steady-state active force against half-sarcomere length (third plot)
- passive force against half-sarcomere length (bottom plot)