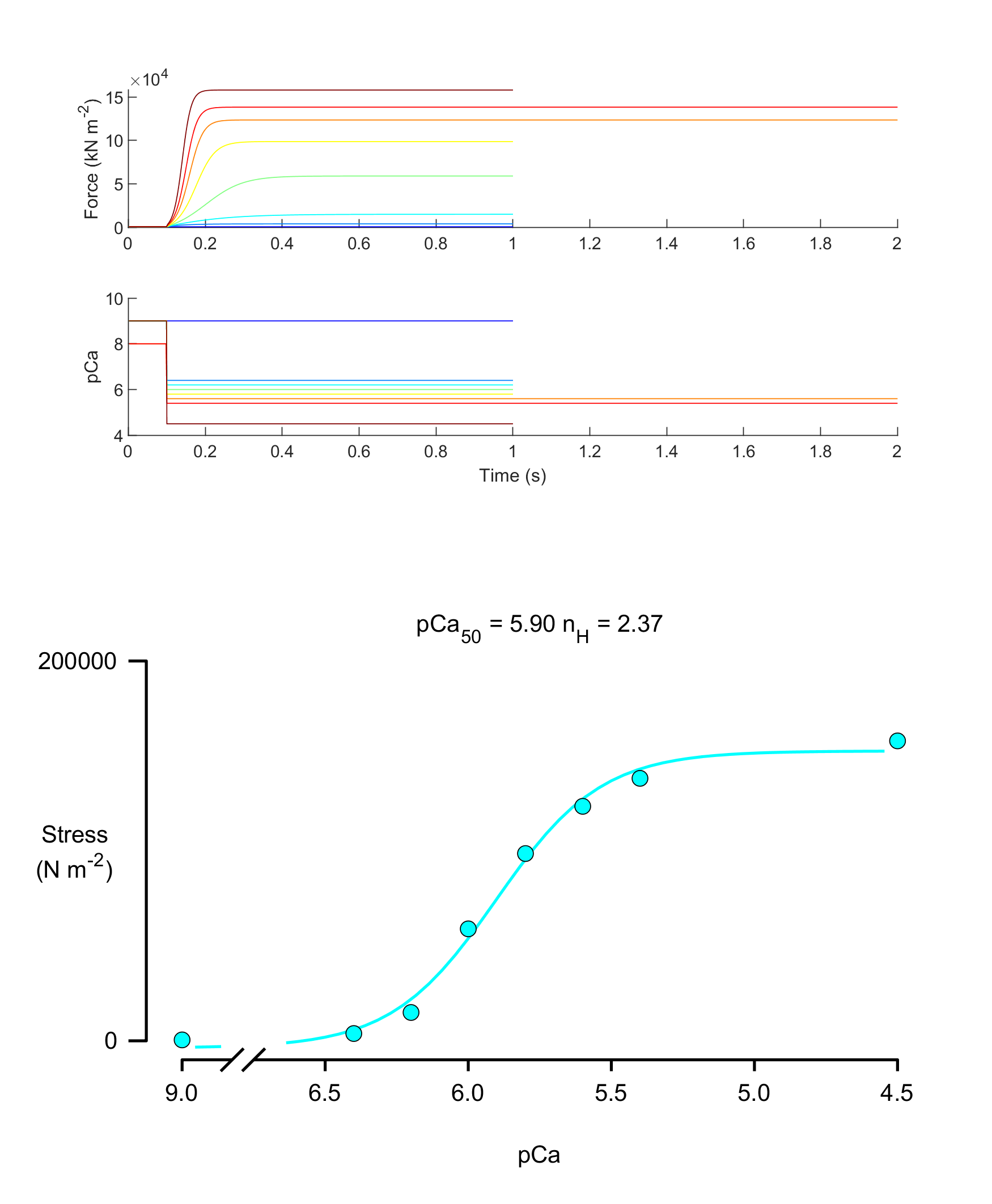
Demo for tension-pCa
Overview
This demo shows how to
- simulate isometric contractions at different levels of Ca2+ activation
- fit a 4-parameter Hill-curve to the steady-state tension data
How this works
The demo initiates a set of simulations using a batch structure.
Each job in the batch defines a single simulation. A snippet of the file is shown here.
{
"MyoSim_batch":
{
"job":
[
{
"protocol_file_string": "sim_input/90/protocol_90.txt",
"model_file_string": "sim_input/model_file.json",
"options_file_string": "sim_input/sim_options.json",
"results_file_string": "../../temp/sim_output/90/results_90.myo"
},
{
"protocol_file_string": "sim_input/64/protocol_64.txt",
"model_file_string": "sim_input/model_file.json",
"options_file_string": "sim_input/sim_options.json",
"results_file_string": "../../temp/sim_output/64/results_64.myo"
},
<SNIP>
]
}
}
Note that every job uses the same
but a different
The results for each job are also written to different output files
Code
If you look at the demo code below, you can see that the function run_batch(batch_data) runs the entire set of simulations. (Behind the science, it uses a MATLAB parfor loop to run simulations on different threads in parallel.)
Once all of the jobs have finished, it is simple to extract the forces from each file and plot the resulting force-pCa curve.
function demo_tension_pCa
% Demo
% Variables
batch_file_string = 'tension_pCa_batch.json';
% Make sure the path allows us to find the right files
addpath(genpath('../../../../code'));
% Load the batch data
batch_json = loadjson(batch_file_string);
batch_data = batch_json.MyoSim_batch;
% Run the batch
run_batch(batch_data);
% Make a figure showing each file and then plot pCa-force curve
% Make a figure
figure(1);
clf;
color_map = jet(numel(batch_data.job));
for i=1:numel(batch_data.job)
% Load data
sim = load(batch_data.job{i}.results_file_string, '-mat');
sim_output = sim.sim_output;
% Plot force and pCa against time
subplot(5, 1, 1);
hold on;
plot(sim_output.time_s, sim_output.muscle_force, '-', ...
'Color', color_map(i,:));
ylabel('Force (kN m^{-2})');
subplot(5, 1, 2);
hold on;
pCa_trace = -log10(sim_output.Ca);
plot(sim_output.time_s, pCa_trace, '-', ...
'Color', color_map(i,:));
ylabel('pCa');
xlabel('Time (s)');
% Keep force and pCa in a structure
curve_data.pCa(i) = pCa_trace(end);
curve_data.y(i) = sim_output.muscle_force(end);
curve_data.y_error(i) = 0;
end
% Fit the tension-pCa curve
[curve_data.pCa50, curve_data.n_H, ...
curve_data.passive_force, curve_data.active_force, ...
curve_data.r_squared, curve_data.x_fit, curve_data.y_fit] = ...
fit_Hill_curve(curve_data.pCa, curve_data.y);
% Plot
title_string = sprintf('pCa_{50} = %.2f n_H = %.2f', ...
curve_data.pCa50, curve_data.n_H);
plot_pCa_data_with_y_errors( curve_data, ...
'axis_handle', subplot(2,1,2), ...
'y_axis_label',{'Stress','(N m^{-2})'}, ...
'y_label_offset', -0.1, ...
'title', title_string);
If you want to extend this demo yourself, the folder also contains a function generate_protocols.m which creates activation protocols for a sequence of pCa values.
Instructions
- Launch MATLAB
- Change directory to the
<repo>\code\demos\getting_started\tension_pCafolder in MATLAB - Open
demo_tension_pCa.m - Press F5 to run the demo
Output